Introduction
Nigeria is a founding member of the Global Methane Initiative (GMI), established in 2004, and provides ongoing support by serving on the Steering Committee and in the Biogas and Oil & Gas Subcommittees.
As a regional leader in climate action, Nigeria has employed a diverse set of strategies to address methane emissions and achieve national and global climate commitments. These efforts are implemented across the oil and gas, agriculture, and energy sectors, and include the adoption of national policies to improve climate resiliency, introduction of regulatory frameworks, and commitment to emissions reduction targets. Nigeria participates in collaborative projects with international partners, aiming to leverage global expertise and resources to enhance its methane management practices and drive sustainable climate solutions.
Nigeria is currently active on the Steering Committee, the Biogas Subcommittee, and the Oil & Gas Subcommittee.
- Introduction
- Methane Emissions Summary
- Methane Commitments and Plans
- Methane Actions
- Ministries and Agencies Supporting Methane Actions
- GMI Delegates
Last Updated: October 2024
Methane Emissions Summary
Methane emissions in Nigeria are projected to increase by about 77% from 2010 under a “business as usual” scenario. In that scenario, the largest share of methane emissions come from residential activities (cooking, lighting, and electricity generation from diesel and gasoline). However, significant methane emission reductions are predicted in alternative scenarios based on successfully achieving all measures included in Nigeria’s National Short Lived Climate Pollutants (SLCP) Plan and Sustainable Energy for All (SE4All) targets.
Methane Emission Sources and Trends, 2010-2050
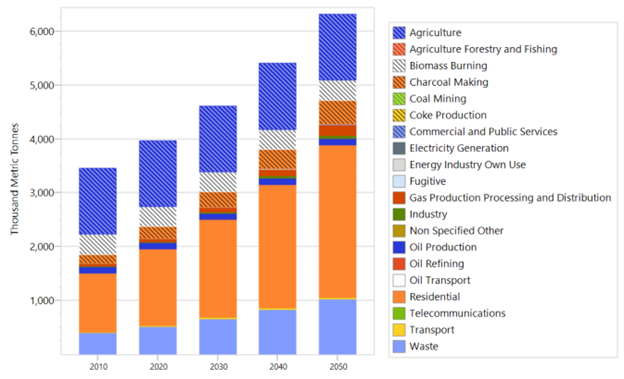
Alternative Scenarios Based on Achievement of Methane Abatement Targets

Source: Federal Republic of Nigeria, Short-lived Climate Pollutants and Opportunities for Mitigation, Accessed September 2024: https://www.ccacoalition.org/policy-database/nigerias-national-action-plan-reduce-short-lived-climate-pollutants
Methane Commitments and Plans
Methane mitigation efforts in Nigeria are guided by national and international commitments and plans. Nigeria also engages in many partnerships dedicated to addressing methane.
National
Nigeria has a national action plan and various climate programs aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to clean energy, and methane mitigation.
- In August 2022, Nigeria unveiled its Energy Transition Plan, a multifaceted approach to achieving a 2060 net-zero target.
- Nigeria published the Long-Term Vision for Nigeria in December 2021, which communicates Nigeria’s plan for a low-emissions future and establishes the government’s commitment to ambitious emission reductions goals. Actions include reduction of gas flaring and fugitive methane emissions, implementation of low-methane fodders for livestock, and use of technology to reduce methane emissions through recovery and use of escaping gas in oil and gas operations.
- Nigeria’s Climate Change Act was signed into law in November 2021, and provides the country with a legal framework to achieve its climate goals.
- The 2021 Update to Nigeria’s First Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), submitted under the Paris Agreement, reflects a more ambitious approach to reducing greenhouse gases in Nigeria, including the country’s commitment to a 60 percent reduction in fugitive methane emissions by 2031.
- In partnership with the Climate and Clean Air Coalition, Nigeria released its National Action Plan to reduce Short-Lived Climate Pollutants (SLCPs) in 2018. The plan contains 22 priority measures to reduce fugitive methane emissions from the oil and gas sector by 61 percent.
- The Federal Ministry of Environment initiated the Renewable Energy Programme to ensure all sectors of the economy make the switch to clean energy sources.
Subnational
Lagos, Nigeria’s largest state, addresses methane emissions reduction strategies through their Climate Action plan which implements a multifaceted approach to monitor and reduce greenhouse gas emissions and achieve specific targets for methane reduction.
- The Lagos State Government released the Lagos Climate Action Plan, 2020-2025 in June 2021.
International Partnerships
Nigeria actively supports and engages with numerous international efforts to address methane challenges.
- Nigeria joined the European Union to launch the Global Methane Pledge (GMP) in 2021 at the United Nations (UN) Climate Change Conference (COP26). As a “GMP Champion,” Nigeria provides leadership to advance the work of the GMP.
- Nigeria joined the Clean Air Task Force in 2019.
- Nigeria joined the Global Methane Alliance in 2018, committing to methane reduction targets of at least 45 percent by 2025.
- Nigeria has participated as a partner in the Climate and Clean Air Coalition since 2012 in support of efforts to address air pollution and promote clean air initiatives.
Methane Actions
The following highlights actions taken by Nigeria to address methane, organized by GMI sector.
Biogas Sector
- The Renewable Energy Roadmap Nigeria promotes the use of community-based biogas digesters and exploration of anaerobic digestion to produce biogas as an alternative energy source to reduce methane emissions. (2023)
Oil & Gas Sector
- The Nigerian Upstream Petroleum Regulatory Commission published its Methane Guidelines for management of fugitive methane and greenhouse gas emissions in upstream oil and gas operations. (2022)
- Nigeria introduced the Nigeria Gas Flare Commercialization Programme (NGFCP) to support the government’s goal of completely eliminating gas flaring and reducing emissions in the oil and gas sectors. The program offers flare gas for sale by the federal government through a competitive bidding process to promote investment in gas flare capture projects. (2022)
- The Petroleum Industry Act established a comprehensive set of policies to reduce the environmental and social impacts of gas flaring and venting of natural gas and methane. (2021)
Cross-Sector
- Nigeria updated the National Climate Change Policy for 2021-2030, which enacts policy measures to reduce methane emissions in the agriculture, oil and gas, waste, and private sectors. The policy implements a goal to eliminate gas flaring completely by 2030. (2021)
- Nigeria was the first African nation to join the BreatheLife Network in 2019, a national Action Plan addressing short-lived climate pollutants.
Ministries and Agencies Supporting Methane Actions
Many Nigerian government agencies address greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, including methane-specific programs. Explore the following websites to learn more.
- Federal Ministry of Environment
- National Environmental Standards and Regulations Enforcement Agency
- Federal Ministry of Petroleum Resources
- Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development
- Federal Ministry of Health
- Federal Ministry of Transport
- Nigerian Upstream Petroleum Regulatory Commission
- Federal Ministry of Works, and Housing
GMI Delegates
| Committee/Subcommittee | Delegate Name | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Biogas Subcommittee | O. A. Afolabi | Nigeria Federal Ministry of the Environment |
| Biogas Subcommittee | Edu Effiom | Cross River State Council on Climate Change |
| Oil & Gas Subcommittee | Abiodun Abdurrahman | Department of Petroleum Resources |
| Oil & Gas Subcommittee | Asmau Jibril | Nigeria Federal Ministry of the Environment |
| Oil & Gas Subcommittee | Olatokunbo Karimu | Department of Petroleum Resources |
| Steering Committee | Bahijjahtu Abubakar | Nigeria Federal Ministry of the Environment |
| Steering Committee | Mohammed Sani | Nigeria Federal Ministry of the Environment |

 Nigeria
Nigeria