Introduction
Australia is a founding member of the Global Methane Initiative (GMI), launched in 2004, and participates in the Biogas and Coal Subcommittees.
Australia has made progress in addressing methane emissions. By implementing innovative practices in agriculture, waste management, and the energy sector, the country has demonstrated their commitment to achieving methane reductions. Notably, Australia's methane emissions have shown a consistent downward trend in recent years, driven by technological advancements and stricter environmental regulations. This steady decline aligns with Australia's broader efforts to reduce its carbon footprint and fulfill its international climate commitments.
Australia is currently active on the Biogas Subcommittee and the Coal Mines Subcommittee.
- Introduction
- Methane Emissions Summary
- Methane Commitments and Plans
- Methane Actions
- Ministries and Agencies Supporting Methane Actions
- GMI Delegates
Last Updated: October 2024
Methane Emissions Summary
Methane (CH4) emissions account for approximately 30% of Australia’s total emissions. As of the quarter ending March 2024, overall methane emission trends have decreased by 12% compared to 2005 levels.
Methane Emissions Trend, September 2004 to March 2024
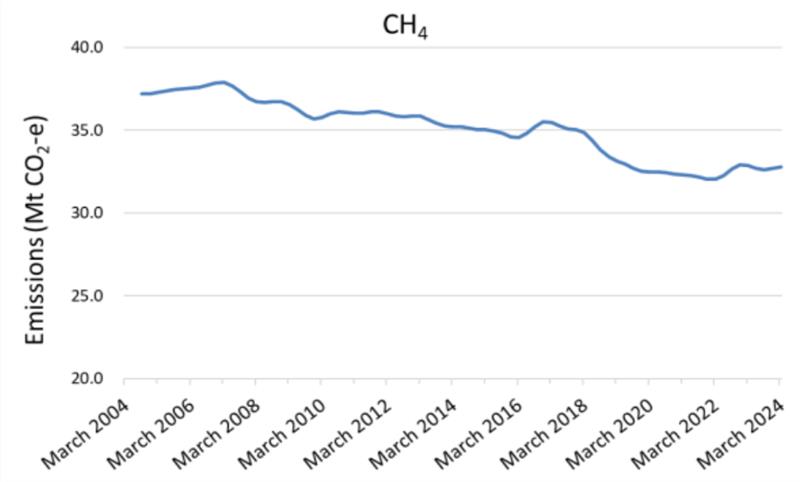
Source: Quarterly Update of Australia’s National Greenhouse Gas Inventory: March 2024, https://www.dcceew.gov.au/sites/default/files/documents/nggi-quarterly-update-march-2024.pdf
Methane Commitments and Plans
Methane mitigation efforts in Australia are guided by international partnerships commitments.
International
Australia has made international commitments to reduce methane emissions.
- Australia joined the Global Methane Pledge in 2021, committing to reducing global methane emissions by 30% from 2020 levels by 2030.
- Australia signed the Paris Agreement on climate change in April 2016, committing to significant measures to cut emissions by 43% below 2005 levels by 2030. The latest quarterly inventory data reflects reductions in methane emissions in the agricultural, oil and gas, and coal mining sectors.
- Australia has been a partner of the Climate and Clean Air Coalition since 2021, supporting activities to reduce methane and other short-lived climate pollutants in the agriculture and oil and gas sectors, among others.
Methane Actions
The following highlights a sampling of actions taken by Australia to address methane, organized by GMI sector.
Biogas Sector
- The Methane Emissions Reduction in Livestock (MERiL) program supports research and awards grants into the use of feed technologies to reduce methane from livestock. (2023)
- Under MERiL, Australia has implemented the Livestock Emissions Framework for Feed Technologies for estimating emission reductions. (2023)
- To support the implementation of the Bioenergy Roadmap, the Australian Government committed an additional $33.5 million to the Australian Renewable Energy Agency to further support Australia’s biogas sector through co-funding additional research, development, and deployment of advanced sustainable biofuels, including biomethane. (2021)
Oil & Gas Sector
- As part of Australia’s broader gas strategy, the country is working to reduce gas-related emissions through close collaboration with the industry and by setting regulations, seeking to limit the venting and flaring of methane in oil and gas operations. (2024)
- On 20 August 2021, Energy Ministers agreed to amend the National Gas Law, National Energy Retail Law and subordinate instruments through an expedited process to bring hydrogen blends, biomethane and other renewable methane gas blends within the national energy regulatory framework.
Cross-Sector
- Australia’s Carbon Credit Unit (ACCU) Scheme provides credits for projects that reduce GHG emissions in several sectors, including projects in the coal or oil and gas sectors that convert methane to carbon dioxide and others in agriculture and waste.
- The Safeguard Mechanism, established in 2016 and reformed in 2023, sets enforceable limits on GHG emissions from Australia’s largest industrial facilities, including landfills, which are significant sources of methane. By targeting these high-emission sites, the policy strengthens Australia’s efforts to meet its emission reduction targets. (2023)
- The Australian Government has committed $8.5 million over 2 years to the Methane Abatement Fund grant program. This initiative supports universities and non-profit organizations in advancing key technologies aimed at reducing methane emissions from the coal and gas sectors. (2023)
- The National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting (NGER) scheme, created under the National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting Act of 2007, is the national framework for reporting company GHG emissions, including methane emissions measurement, reporting, and verification, energy production, and energy consumption. The data that companies report is used to prepare the national GHG inventory and ensures that companies are not exceeding emissions limitations. (2007)
Ministries and Agencies Supporting Methane Actions
Many Australian government agencies address greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, including methane-specific programs. Explore the following websites to learn more.
- NSW Environmental Protection Authority
- Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water
- Department of Water and Environmental Regulation
- Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety
- Department of Planning, Lands and Heritage
- Department of Agriculture, Fisheries, and Forestry
- Department of Global Affairs and Trade
GMI Delegates
| Committee/Subcommittee | Delegate Name | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Coal Subcommittee | Hua Guo | The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) |

 Australia
Australia