Introduction
China is a founding member of the Global Methane Initiative (GMI), launched in 2004, and provides ongoing support by participating in the Steering Committee and by serving in a leadership role on the Coal Mines Subcommittee.
As part of its Methane Emission Control Plan, China has launched several initiatives to reduce methane emissions, including efforts to capture coal bed gas from the coal-mining sector, improve waste management practices on livestock farms, enhance urban waste treatment processes, and strengthen monitoring and reporting systems to assess the effectiveness of these methane reduction strategies. The plan also includes the establishment of strategic policies and the promotion of clean energy technologies like anaerobic digestion. By integrating these strategies, China is working towards its national climate goals while contributing to global efforts in climate action and sustainability.
China is currently active on the Steering Committee and the Coal Mines Subcommittee (Co-Chair).
- Introduction
- Methane Emissions Summary
- Methane Commitments and Plans
- Methane Actions
- Ministries and Agencies Supporting Methane Actions
- GMI Delegates
Last Updated: November 2024
Methane Emissions Summary
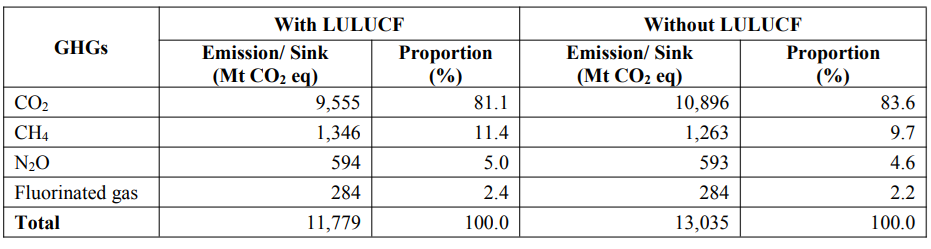
According to the People’s Republic of China Third Biennial Update Report on Climate Change, published in December 2023, methane emissions accounted for 11.4% of China’s total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2018, totaling 1,346 Mt CO2 eq.
GHG Emissions by Gas, 2018
GHG Emissions by Sector, 2018
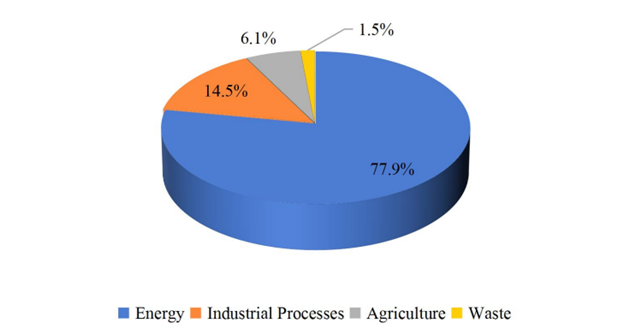
Source: The People’s Republic of China Third Biennial Update Report on Climate Change, accessed September 2024, https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/resource/China_BUR3_English.pdf
Methane Commitments and Plans
National
China has implemented national action plans and strategies aimed at mitigating GHG emissions and advancing sustainable development.
- In November 2023, China released its Methane Emissions Control Action Plan, a national strategy focused on improving emissions monitoring, reducing methane emissions in the energy sector, and enhancing the sustainability of livestock and manure management.
- The report China’s Achievements, New Goals, and New Measures for Nationally Determined Contributions, published in October 2021, outlines China's progress toward reducing carbon emissions, including significant investments in renewable energy and green technology. It also details China's updated targets, such as peaking carbon emissions before 2030 and achieving carbon neutrality by 2060, supported by enhanced monitoring, emissions trading, and industry-specific standards.
International
China is actively collaborating with international partners and engages in activities to establish significant climate goals to confront pressing environmental issues.
- The Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (MEE) and the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) signed a Memorandum of Understanding in June 2023 to enhance their collaborative efforts in tackling the challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution.
- China signed the Paris Agreement on climate change in April 2016, committing to significant measures to combat climate change. Specifically, China aims to cut its carbon emissions per unit of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by 60-65% by 2030 from 2005 levels, increase the share of non-fossil fuels in primary energy consumption to roughly 20%, and ensure that carbon emissions reach their maximum level by 2030.
- China contributes expertise to the UN Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), including support for the UNECE Group of Experts on Coal Mine Methane and Just Transition. In addition, the International Centre of Excellence on Coal Mine Methane, a collaborative partnership between UNECE and China was launched in 2017. The ICE-CMM serves as a regional and international center for best practices in gas capture and utilization.
Methane Actions
The following highlights actions taken in China to address methane, organized by GMI sector.
Biogas Sector
- China aims to utilize at least 80% of livestock waste by 2025, with a focus on constructing anaerobic digesters to capture methane from manure. (2023)
- The Regulations on Urban Drainage and Sewage Treatment enhance wastewater management and protect public health by requiring municipalities to develop comprehensive drainage and sewage treatment plans. The regulations establish standards, focusing on reducing pollutants, including methane emissions from sewage systems. By promoting public participation and ensuring compliance, these regulations support sustainable urban development and environmental protection. (2014)
Coal Mines Sector
- China aims to strengthen the comprehensive utilization of methane. By 2025, the annual utilization of coal mine methane will reach 6 billion cubic meters. (2023)
- The Shenmu-Anping Methane Pipeline, completed in 2021, is China’s largest coal bed methane pipeline, designed to capture and transport methane for energy use as part of a broader initiative to utilize 6 billion cubic meters of coal bed gas by 2025. (2021)
- With the support of tax incentives and exemptions, and financial subsidies, the coal industry in China has enforced strict emission standards of coal mine methane, promoted resource utilization to encourage emissions reduction, and organized demonstrations of efficient methane drainage and utilization technologies, so as to facilitate the recovery and utilization of coal bed methane and coal mine methane.
Oil & Gas Sector
- As part of China’s Methane Emissions Control Plan, the country is promoting the implementation of leak detection and repair technologies in the oil and gas sector to enhance leak detection, improve maintenance capabilities, and increase pipeline efficiency. Additionally, the initiative facilitates the gradual reduction of conventional flaring in oil and gas systems. (2023)
- To better control methane emissions in the oil and gas industry, the major Chinese oil and gas companies founded the China Oil and Gas Methane Alliance. (2021)
Cross Sector
- The State Council's action plan for energy conservation and carbon reduction during 2024-25 is intended to cut energy consumption by 2.5% and carbon emissions by 3.9% per GDP unit. The plan targets a 3.5% reduction in major industries and seeks to increase non-fossil energy use to 18.9%. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, the plan also strives to lower methane emissions, supporting climate goals while saving 50 million tons of standard coal and reducing carbon emissions by 130 million tons. (2024)
- China's greenhouse gas observation network supports its goals of carbon peaking by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060. By monitoring real-time emissions, including methane, it enables data-driven decisions for effective emission reduction strategies.
- China explores promoting the development of the carbon trading market, incentivizing companies to reduce methane emissions through market mechanisms.
Ministries and Agencies Supporting Methane Actions
Many government ministries address greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, including methane-specific programs. Explore the following websites to learn more.
GMI Delegates
| Committee/Subcommittee | Delegate Name | Affiliation |
|---|---|---|
| Biogas Subcommittee | Dong Baocheng | Rural Energy & Environment Agency |
| Biogas Subcommittee | Xu Haiyun | China Urban Construction Design and Research Institute |
| Coal Subcommittee | Liu Wenge | China Coal Information Institute (CCII) |
| Steering Committee | Liu Wenge | China Coal Information Institute (CCII) |
| Steering Committee | Liu Yang | China Ministry of Ecology and Environment |

 China
China